What is blockchain ? how does blockchain work? how does bitcoin work? pros-cons of block chain technology.
What is blockchain ?
Blockchain: a method of storing data amongst multiple parties that ensures data integrity which means that blockchain is a method of storing data through various computers around the world.
When someone says "blockchain", they typically mean
- The technology behind cryptocurrencies that is receiving attention because of its immutability and transparency
- Data committed to blockchain cannot be changed.
- A "distributed ledger", or a shares database where everyone holds a copy
Bitcoin is powered by open-source code known as block chain, which creates a shared public ledger. Each transaction is a “block” that is “chained” to the code, creating a permanent record of each transaction. Block chain technology is at the heart of more than 10,000 crypto currencies that have followed in Bitcoin’s wake.
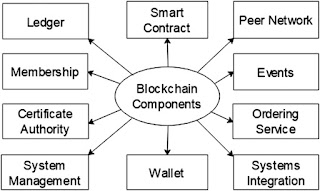
Blockchain components :
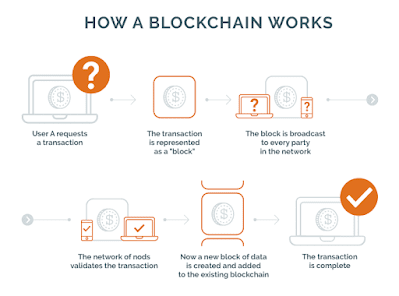
How does blockchain work?
- User A request a transaction
- The transaction is represented as a "block"
- The block is broadcast to every party in the network
- The network of nodes validates the transaction
- Now a new block of data is created and added to the existing blockchain
- The transaction is complete
How does Bitcoin work?
From a user perspective, Bitcoin is nothing more than a mobile app or computer program that provides a personal Bitcoin wallet and allows a user to send and receive bitcoins with them. This is how Bitcoin works for most users.
- Download software onto computer or phone
- Software will generate unique address
- You buy bitcoin the funds are added to your digital wallet
- Bitcoin network authenticates transactions
- You may now use your bitcoin to pay online
Behind the scenes, the Bitcoin network is sharing a public ledger called the "block chain". This ledger contains every transaction ever processed, allowing a user's computer to verify the validity of each transaction. The authenticity of each transaction is protected by digital signatures corresponding to the sending addresses, allowing all users to have full control over sending bitcoins from their own Bitcoin addresses. In addition, anyone can process transactions using the computing power of specialized hardware and earn a reward in bitcoins for this service. This is often called "mining".
Reference : Bitcoin.org
Pros and cons of blockchain technology
(1) PROS :
- security
- Transparency
- Accessibility
- Decentralization
- Applications in numerous sectors
Cash-like: easy to transfer. secure, and authenticate
Extremely Fast Settlement much faster than ACH, SWIFT, Wire Transfer, and credit settlement time frames
Shiny and New- earthy adopter grow; high disruption potential: extremely sophisticated technology
Inflation Resistant: limited supply of Bitcoins protects against inflation
Low Transaction Costs: enables true micro payments
Extremely Secure: built on state of the art encryption standards: (same schemes used by banks, ISPS. etc.)
Regulatory Approval: US Senate Hearings; IRS; many U.S. states already granting license to exchanges
Decentralized, distributed network: Internet-like resilience
Decentralization:
(2) cons :
- Speed of transactions
- Energy cost
- Servers capacity
- Recentralization
- Lack of regulation and control body
Cash-like: vulnerable to loss, theft
Transactions Final, Irreversible
Slower Verification: card-based authorization in mili-seconds: fulI Bitcoin transaction verification at least 10 minutes, more for larger transactions
Slow Adoption: not well understood: lack of trust in currency not backed by govt: regulatory concerns
Bitcoins Scarce by Design: price fluctuation, settlement risk, hoarding
Transaction Fee Problem: sufficient reward for miners once last Bitcoin has been minted
Regulatory Uncertainty: FinCEN and KYC: consumer protection concerns
" The Blockchain does one thing: It replaces third-party trust with mathematical proof that something happened." - ADAM DRAPER


Comments
Post a Comment